관련된 포스팅
JAVA Basic) 제네릭(Generic)
목차 <제네릭?> 프로그램에서 변수를 선언할 때, 메서드에서 매개 변수를 사용할 때도 모든 변수는 자료형이 있다. 대부분은 하나의 자료형으로 구현하지만, 변수나 메서드의 자료형을 필요에
montoo.tistory.com
JAVA Basic) 컬렉션 프레임워크
목차 <컬렉션 프레임워크란?> 흔히 프로그래밍을 건축에 비유를 한다. 원하는 건물을 지으려면 구조를 잘 잡아야하듯, 프로그램 개발도 사용하는 자료를 어떤 구조로 관리할 것인지가 중요하기
montoo.tistory.com
JAVA Basic) 컬렉션 프레임워크 - List 인터페이스
'컬렉션 프레임워크'가 뭔지 모른다면, 아래 포스트부터 확인할 것 흔히 프로그래밍을 건축에 비유를 한다. 원하는 건물을 지으려면 구조를 잘 잡아야하듯, 프로그램 개발도 사용하는 자료를 어
montoo.tistory.com
JAVA Basic) 컬렉션 프레임워크 - Set 인터페이스
이해가 되지 않을 경우 이전 포스팅을 참고하세요. 2021.10.05 - [Programming/JAVA 기초] - JAVA Basic) 컬렉션 프레임워크 흔히 프로그래밍을 건축에 비유를 한다. 원하는 건물을 지으려면 구조를 잘 잡아
montoo.tistory.com
JAVA Basic) 컬렉션 프레임워크 - Map 인터페이스
컬렉션 프레임워크의 배경 지식은 이전 포스트를 참고하시길 바랍니다. 흔히 프로그래밍을 건축에 비유를 한다. 원하는 건물을 지으려면 구조를 잘 잡아야하듯, 프로그램 개발도 사용하는 자료
montoo.tistory.com
목차
Q1.
자료 구조를 사용하기 편리하도록 자바에서 제공하는 라이브러리를 [ ]라고 한다.
Q2.
클래스에서 여러 자료형을 사용할 때 자료형을 명시하지 않고 자료형을 의미하는 문자로 선언한 후 실제 클래스를 생성할 때 자료형을 명시하는 프로그래밍 방식을 [ ]이라고 한다.
Q3.
Collection 인터페이스를 구현한 클래스를 순회하기 위해 사용하는 인터페이스는 [ ] 이다.
Q4.
TreeSet을 사용할 때 Comparable 인터페이스를 구현해야 하는 이유를 설명하세요.
Q5.
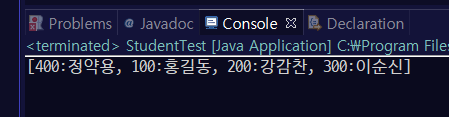
StudentTest의 출력 결과가 다암처럼 나오도록 Student 클래스를 구현해 보자.
public class StudentTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashSet<Student> set = new HashSet<Student>();
set.add(new Student("100", "홍길동"));
set.add(new Student("200", "강감찬"));
set.add(new Student("300", "이순신"));
set.add(new Student("400", "정약용"));
set.add(new Student("100", "송중기"));
System.out.println(set);
}
}
Q6.
다음 코드에서 CarTest의 테스트 결과가 true, true, false가 되도록 HashMap을 사용해 CarFactory 클래스를 구현해 보자.
Car 클래스
public class Car {
String name;
public Car() {}
public Car(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
CarTest 클래스
public class CarTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
CarFactory factory = CarFactory.getInstance();
Car sonata1 = factory.createCar("연수 차");
Car sonata2 = factory.createCar("연수 차");
System.out.println(sonata1 == sonata2); //true
Car avante1 = factory.createCar("승연 차");
Car avante2 = factory.createCar("승연 차");
System.out.println(avante1 == avante2); //true
System.out.println(sonata1 == avante1); //false
}
}
정답:
Q1:
컬렉션 프레임워크
Q2:
제네릭 프로그래밍
Q3:
Iterator
Q4:
Tree구조는 기본적으로 자료를 비교하여 구조화한 방식이기 때문에 자료를 비교할 수 있는 Comparable 또는 Comparator 인터페이스를 구현해야한다.
Q5:
Student 클래스
package practice.q5;
public class Student {
private String StudentId;
private String StudentName;
public Student(String studentId, String StudentName) {
this.StudentId = studentId;
this.StudentName = StudentName;
}
public String getStudentId() {
return StudentId;
}
public void setStudentId(String studentId) {
StudentId = studentId;
}
public String getStudentName() {
return StudentName;
}
public void setStudentName(String studentName) {
StudentName = studentName;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if(obj instanceof Student) {
Student std = (Student)obj;
if(std.StudentId == this.StudentId) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return Integer.parseInt(StudentId); //parsInt()메서드로 String 숫자를 정수형으로 변환
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return StudentId + ":" + StudentName ;
}
}
Q6:
import java.util.HashMap;
public class CarFactory {
static CarFactory inst;
HashMap<String, Car> hashMap = new HashMap<>();
public static CarFactory getInstance() {
inst = new CarFactory();
return inst;
}
public Car createCar(String name) {
if(hashMap.containsKey(name)) {
return hashMap.get(name);
}
Car car = new Car();
hashMap.put(name, car);
return car;
}
}